Example of the use of GIS
Map of potential erosion for Puerto Rico
Soil contains the essential nutriments, minerals and organic material required for plant growth. These could be lost by erosion if not properly managed. The soil lost can be estimated with the use of mathematical models. One of the most widely used models is the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE).
Because of the spatial nature of soil and soil erosion, GIS technology, together with an erosion model can be used to identify potential areas of soil erosion so these areas can be targeted first.
Highly Erodible Lands (HEL)
The erodibility index (EI) for a soil map unit is determined using a modification to the RUSLE equation and the soil loss tolerance (maximum amount of soil that can be lost for a soil in a year) as presented in the Food Security Act Manual (USDA, 1994).
Where:
R = rainfall and runoff erosibity for geographical location.
K = soil erodibility factor.
LS = slope length and steepness factor.
T = soil loss tolerance value
Highly Erodible Lands (HEL) are those with an EI higher than 8.
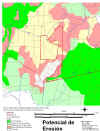
Press on the map to enlarge.
Even though the following picture looks like a oblique aerial photo, it was prepared using GIS technology. A satellite image, which is a flat image is put together with the Digital Elevation Model (DEM) which is a GIS file with the topography or elevations of the area. The program takes into account the elevation to simulate a perpendicular view of the area. Besides, it could be use to simulate like if you were flying above the area in real time.
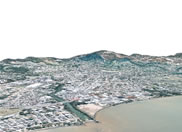
|